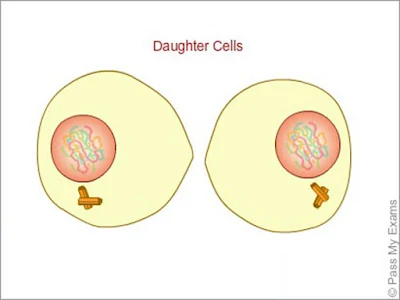
Mitosis is a somatic or vegetative cell division and
the daughter cells resemble the mother
cell in every aspect. Organs formed by this type of division such as liver,
kidney, brain, skin, etc. are called vegetative organs because they do not
participate directly in reproduction.
Growth of any organ system in plant or animal is due
to increase in cell number by mitosis. Cells from young ad tender organs such
as shoot, tips, bud, root tips, tissues of young animals the divided more
rapidly than the cell from old and mature organs. This is the reason for a
greater rate of growth in young organs .
Before the cell division occurs various changes are
seen in the cell. Major change is the doubling of the number of chromosomes.
Only after this is completed, the cell divide, so the the daughter cell will
have the same number of chromosomes as the mother cells..
This is essential you have already learnt that
chromosomes carry the genes. Genes carry the genetic information and are
responsible for the inheritance of
parental features. They also regulate all the function of the cell by directing
and controlling all the proteins in the cells.
Before cell division begins, the non-diving or
resting cells are said to be in interphase. This phase in the life of the cell
is called interphase.
Chromosomes in the nucleus of interphase cell are in
a highly decondensed state and form a diffuse network of filaments called
chromatin. Most of the cells spend a
considerable portion of their life in interphase.Mitosis is of brief duration
and once the division is complete, both the daughter cells usually enter into
interphase.
Once mitosis is initiated it proceeds without any
interruption till the cell division is complete and daughter cells are
formed.Based on the changes occurring in the five stages have been recognized
in mitosis .1. prophase 2. Metaphase 3. Anaphase 4. Telophase
and 5. Cytokinesis.
Prophase :
This is
the first stage of cell division. Before prophase starts the chromosomes are in
a decondensed state and appear as a diffuse network of filaments. During
prophase, the chromosomes start condensing.
As a results, the shape of the chromosomes becomes
definite and distinct. Each chromosomes has two arms called chromatids. The two
chromatids are joined together by centromere. While these changes are occurring
the nucleous and rest of the structure in the
nucleus disappear gradually.
Meanwhile the centrioles move to the opposite side of nucleus. In plants cells,
where centrioles are usually absent the they appear at this stage of cell
division. From each centriole fine thread like fibres appear. These fibres are
called spindle fibres. Acentriole with spindle fibres is called an aster. The
spindle fibres grow towards the centre of the cell.
2. Metaphase:
Chromosomes now move to the centre of the cell and
arrange themselves in a row. This looks like a plate and is called quitorial
plate. Some of the spindle fibres are attached to the centromere of each chromosome. Rest of the
fibres grow towards opposite pole and join the centriole on the opposite side.
Each chromosome is attached to fibres from the two opposite poles.
3. Anaphase:
At this spindle fibres pull the chromosomes to
opposite ends. As a results the centromere splits and are pulled a part along
with chromatids. As a result, half the original number of chromosomes move to each of the two opposite poles.
4. Telophase:
By the beginning of this phase, the chromosomes
complete movement and will be at each end of the cell. Nuclear membrane,
nucleolus and other nuclear structure reappear. Chromosomes begin decondensation
process. By the end of telophase, cell will be having two nuclei, one on each
side. Spindle fibres now disappear.
5. Cytotinesis:
A new membrane is formed at the quitorial plate
during this phase. This didivide the cell in two daughter cells. Thus at the
end of mitosis, two daughter cells which are extractly similar to the mother
cell are formed. This first four stages of cell division involve changes in nucleus
and division of nuclear components equally between daughter cells.
Hence, these
four phases prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase of cell division
are together called karyokinesis. Means division of nucleus. The last stage is called cytokinesis
as the cytoplasm is the only component undergoing division in this stage of
mitosis.
POINTS TO REMEMBER:
Mitosis
is a somatic cell.
Doubling
of the number of chromosomes is the major event before cell division.
Interphase
is the period when the cell grows in size nd performs the physiological
functions. Chromation is in a decondensed state in the nucleus of an interphase
cell.
During
prophase, centrioles move to the opposite poles of the cells and spindle fibres
formed from the centrioles.
During
metaphase, chromosomes move to centre of
the cell and form equatorial plate. Spindle
fibres grow in length and attach themselves to the centromere of each chromosome..
During
anaphase, the chromosomes are pulled apart and each half moves to the opposite
side of the cell.
During
telophase, the nuclear membrane appears around the chromosomes and chromosomes
decondense into chromatin.
During
cytokinesi, a membrane or a cell wall appears in the middle of the cells and
divides the cytoplasm of the cell into two. With this the cell division is
completed and two daughter cells are formed. During
mitosis, kayokinesis occurs before cytokinesis.
THANKYOU,