This website provides content designed to align with a variety of educational syllabi, including CBSE, SSC across India, and Common Core curricula from major countries. We aim to serve teachers, parents, students, and educational institutions by offering resources that enhance the quality of education. Our mission is to make learning more engaging and enjoyable, ensuring subjects are not only interesting but also deeply insightful.
Pages
NEET IIT
Monday, March 14, 2016
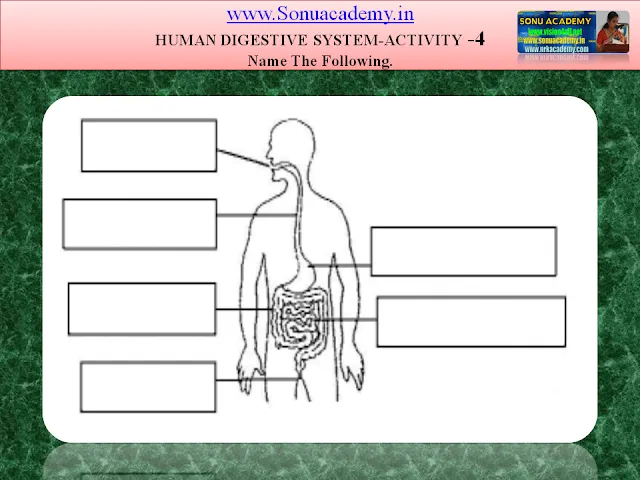
HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM- ACTIVITY-4
 Nanditha completed her Masters in Zoology, English, and Education. She is multifaceted and has an abiding interest in children and education. She is a vibrant and enthusiastic teacher and has a unique ability to draw the attention of children to the subject at hand. Her primary goal is to carry out deep studies on the effect of a child centric and holistic education on students. Herself a skilled teacher in multiple subjects she wants her researches to sensitize the world to the infinite powers inherent in the child. She has done a marvelous work in ICT education. Received “International Academic and Research Excellence Award (IARE 2019) by GISR, ‘Research in Education Award’ by EIA-2019, ‘National Education Leadership Award’- 2019, ‘Best Young Researcher Award’ GERA 2019 and ‘South Indian women’s Achiever Award’.
www.sonuacademy.in
www.nrkacademy.com
www.thehindiacademy.com
www.ibcurriculum.in
Nanditha completed her Masters in Zoology, English, and Education. She is multifaceted and has an abiding interest in children and education. She is a vibrant and enthusiastic teacher and has a unique ability to draw the attention of children to the subject at hand. Her primary goal is to carry out deep studies on the effect of a child centric and holistic education on students. Herself a skilled teacher in multiple subjects she wants her researches to sensitize the world to the infinite powers inherent in the child. She has done a marvelous work in ICT education. Received “International Academic and Research Excellence Award (IARE 2019) by GISR, ‘Research in Education Award’ by EIA-2019, ‘National Education Leadership Award’- 2019, ‘Best Young Researcher Award’ GERA 2019 and ‘South Indian women’s Achiever Award’.
www.sonuacademy.in
www.nrkacademy.com
www.thehindiacademy.com
www.ibcurriculum.in
HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM- ACTIVITY-3
 Nanditha completed her Masters in Zoology, English, and Education. She is multifaceted and has an abiding interest in children and education. She is a vibrant and enthusiastic teacher and has a unique ability to draw the attention of children to the subject at hand. Her primary goal is to carry out deep studies on the effect of a child centric and holistic education on students. Herself a skilled teacher in multiple subjects she wants her researches to sensitize the world to the infinite powers inherent in the child. She has done a marvelous work in ICT education. Received “International Academic and Research Excellence Award (IARE 2019) by GISR, ‘Research in Education Award’ by EIA-2019, ‘National Education Leadership Award’- 2019, ‘Best Young Researcher Award’ GERA 2019 and ‘South Indian women’s Achiever Award’.
www.sonuacademy.in
www.nrkacademy.com
www.thehindiacademy.com
www.ibcurriculum.in
Nanditha completed her Masters in Zoology, English, and Education. She is multifaceted and has an abiding interest in children and education. She is a vibrant and enthusiastic teacher and has a unique ability to draw the attention of children to the subject at hand. Her primary goal is to carry out deep studies on the effect of a child centric and holistic education on students. Herself a skilled teacher in multiple subjects she wants her researches to sensitize the world to the infinite powers inherent in the child. She has done a marvelous work in ICT education. Received “International Academic and Research Excellence Award (IARE 2019) by GISR, ‘Research in Education Award’ by EIA-2019, ‘National Education Leadership Award’- 2019, ‘Best Young Researcher Award’ GERA 2019 and ‘South Indian women’s Achiever Award’.
www.sonuacademy.in
www.nrkacademy.com
www.thehindiacademy.com
www.ibcurriculum.in
Sunday, March 13, 2016
HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM- ACTIVITY- 2
 Nanditha completed her Masters in Zoology, English, and Education. She is multifaceted and has an abiding interest in children and education. She is a vibrant and enthusiastic teacher and has a unique ability to draw the attention of children to the subject at hand. Her primary goal is to carry out deep studies on the effect of a child centric and holistic education on students. Herself a skilled teacher in multiple subjects she wants her researches to sensitize the world to the infinite powers inherent in the child. She has done a marvelous work in ICT education. Received “International Academic and Research Excellence Award (IARE 2019) by GISR, ‘Research in Education Award’ by EIA-2019, ‘National Education Leadership Award’- 2019, ‘Best Young Researcher Award’ GERA 2019 and ‘South Indian women’s Achiever Award’.
www.sonuacademy.in
www.nrkacademy.com
www.thehindiacademy.com
www.ibcurriculum.in
Nanditha completed her Masters in Zoology, English, and Education. She is multifaceted and has an abiding interest in children and education. She is a vibrant and enthusiastic teacher and has a unique ability to draw the attention of children to the subject at hand. Her primary goal is to carry out deep studies on the effect of a child centric and holistic education on students. Herself a skilled teacher in multiple subjects she wants her researches to sensitize the world to the infinite powers inherent in the child. She has done a marvelous work in ICT education. Received “International Academic and Research Excellence Award (IARE 2019) by GISR, ‘Research in Education Award’ by EIA-2019, ‘National Education Leadership Award’- 2019, ‘Best Young Researcher Award’ GERA 2019 and ‘South Indian women’s Achiever Award’.
www.sonuacademy.in
www.nrkacademy.com
www.thehindiacademy.com
www.ibcurriculum.in
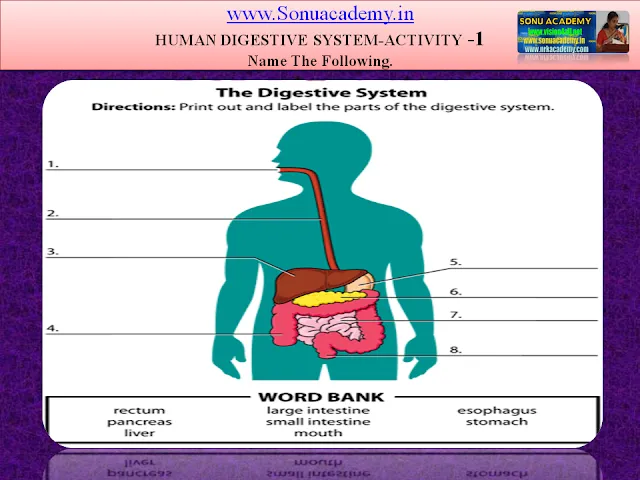
HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM- ACTIVITY-1
 Nanditha completed her Masters in Zoology, English, and Education. She is multifaceted and has an abiding interest in children and education. She is a vibrant and enthusiastic teacher and has a unique ability to draw the attention of children to the subject at hand. Her primary goal is to carry out deep studies on the effect of a child centric and holistic education on students. Herself a skilled teacher in multiple subjects she wants her researches to sensitize the world to the infinite powers inherent in the child. She has done a marvelous work in ICT education. Received “International Academic and Research Excellence Award (IARE 2019) by GISR, ‘Research in Education Award’ by EIA-2019, ‘National Education Leadership Award’- 2019, ‘Best Young Researcher Award’ GERA 2019 and ‘South Indian women’s Achiever Award’.
www.sonuacademy.in
www.nrkacademy.com
www.thehindiacademy.com
www.ibcurriculum.in
Nanditha completed her Masters in Zoology, English, and Education. She is multifaceted and has an abiding interest in children and education. She is a vibrant and enthusiastic teacher and has a unique ability to draw the attention of children to the subject at hand. Her primary goal is to carry out deep studies on the effect of a child centric and holistic education on students. Herself a skilled teacher in multiple subjects she wants her researches to sensitize the world to the infinite powers inherent in the child. She has done a marvelous work in ICT education. Received “International Academic and Research Excellence Award (IARE 2019) by GISR, ‘Research in Education Award’ by EIA-2019, ‘National Education Leadership Award’- 2019, ‘Best Young Researcher Award’ GERA 2019 and ‘South Indian women’s Achiever Award’.
www.sonuacademy.in
www.nrkacademy.com
www.thehindiacademy.com
www.ibcurriculum.in
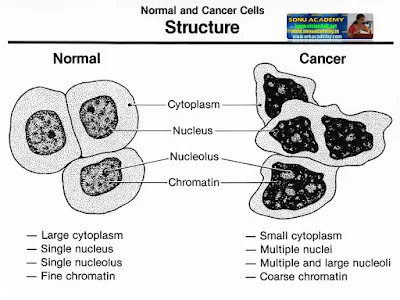
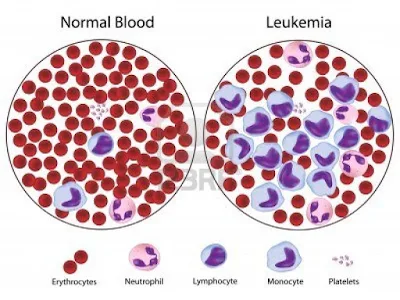
CANCER -TEXT
In the last lesson, you have learnt the importance
of cell division. Usually the cell division as rapid and occurs for large
number of times in young and developing animals.
As a result, the organisms grow in size. As the
organism becomes an adult, the cell division in several tissues slows down
considerably.
Some tissues may completely stop dividing. In several tissues of
adult organisms, cell division occurs only when it is required- like in injury.
Thus cell division is a highly controlled process.
However, some times this control over cell division
is lost. Then the cell goes on dividing without any control. Due to this, a
large mass of cells are formed. Such a mass of cells is called a tumor. These cells
in the tumor compete with other normal cell in the body for space and
nutrients and even kill the normal cells.
Some times, the tumor is enclosed in a layer of
connective tissue and does not spread. Such tumors are called benign tumors.
They are usually harmless and are removed by surgery.
Cancer can affect any tissue in the body at any age.
If the cancer affects the epithelial cells that cover the body organs, then it
is called carcinoma. Cancer or lung, breast, pancreas and stomach are examples
for carcinoma.
If cancer affects the tissues like muscle, lymph
nodes then it is called sarcoma. Cancer affecting blood cells, especially of
white blood cells is called leukemia.
Cancer is not a contagious disease. It does not
spread from person to person. Cancer is not an inherited disease. The major change in the genetic material (DNA)of the
cell. A change in the DNA is called mutation. Mutations occur due to several
reasons. It must be remembered that not all mutations results in cancer. Only
certain mutations lead to cancerous growth. There are three types of agents that cause cancer.
They are physical, chemical and biological agents. Agents that cause cancer are
called carcinogenic gents. As cancer is caused by more than one agent, there is
no single cure for cancer.
Depending on the type, location in the body and
severity, various methods are used to treat cancer. It removed by surgery or
cancer cells are killed by carefully exposing them to very strong X- rays or
gamma –rays for brief periods and also with drugs called anti-cancer drugs.
Even these treatments cannot cure cancer completely.
Among men, cancer of Digestive system especially of
mouth and throat and lungs are the major types of cancer. In women, cancer of
cervix and breast cancer are more common.
Tobacco – smoking and gutka – chewing:
In India, amongst the social health problems,
diseases due to consumption of tobacco product and smoking are important . if
the present kind of consumption of tobacco is continued it is estimated that
2.4 lakhs of population will suffer with cancer.
Student and youth take up smoking and tobacco
(gutka) chewing due to eer pressure. Though smoking and chewing gutka cause
some discomfort in the first attempt they are addictive in nature. Further
“nicotine” which present in tobacco, gives a kind energy but gradually weakens
the body.
Consumption of tobacco products:
It affect the central nervous sytem
Causes heart diseases, mental retardation,
psychological depression, feeling of insecurity, paralysis and acute neutitis.
Causes lung cancer, oral cancer, gastrao intestinal
track cancer etc.
Preganant woment may give birth to mentally
retarted, low birth weight and babies with deformities.
It is therefore necessary that students do not
consume tobacco products, and also enlighten users about the bad effects of
tobacco consumption..
Cancer can be indentified at very early
stages by the following sysmptoms.
Cough lasting for more than 2 weeks
A persistent change in bowl habits.
Unexplained loss of weight and appetite
Sudden growth of a mole or wart.
A hard lump
in the breast.
Excessive
loss of food.
Sore throat and harness’ in voice.
Healthy habits, such as not smoking and not suing
tobacco products, not consuming alcohol, proper diet and regular physical
exercise can prevent the occurrence of cancer to some extent.
THANKYOU,
NANDITHA AKUNURI
NANDITHA AKUNURI
 Nanditha completed her Masters in Zoology, English, and Education. She is multifaceted and has an abiding interest in children and education. She is a vibrant and enthusiastic teacher and has a unique ability to draw the attention of children to the subject at hand. Her primary goal is to carry out deep studies on the effect of a child centric and holistic education on students. Herself a skilled teacher in multiple subjects she wants her researches to sensitize the world to the infinite powers inherent in the child. She has done a marvelous work in ICT education. Received “International Academic and Research Excellence Award (IARE 2019) by GISR, ‘Research in Education Award’ by EIA-2019, ‘National Education Leadership Award’- 2019, ‘Best Young Researcher Award’ GERA 2019 and ‘South Indian women’s Achiever Award’.
www.sonuacademy.in
www.nrkacademy.com
www.thehindiacademy.com
www.ibcurriculum.in
Nanditha completed her Masters in Zoology, English, and Education. She is multifaceted and has an abiding interest in children and education. She is a vibrant and enthusiastic teacher and has a unique ability to draw the attention of children to the subject at hand. Her primary goal is to carry out deep studies on the effect of a child centric and holistic education on students. Herself a skilled teacher in multiple subjects she wants her researches to sensitize the world to the infinite powers inherent in the child. She has done a marvelous work in ICT education. Received “International Academic and Research Excellence Award (IARE 2019) by GISR, ‘Research in Education Award’ by EIA-2019, ‘National Education Leadership Award’- 2019, ‘Best Young Researcher Award’ GERA 2019 and ‘South Indian women’s Achiever Award’.
www.sonuacademy.in
www.nrkacademy.com
www.thehindiacademy.com
www.ibcurriculum.in
MEIOSIS AND REDUCTION DIVISION - TEXT
You have learnt
that meiosis is the reduction division and occurs in the germ cells that
produce gamets. Majot difference between mitosis and meiosis is in the number
of chromosomes in daughter cells.
In mitosis, daughter cells have exactly the
same number of chromosomes as the mother cell while, in meiosis the daughter
cells have half the number of chromosomes of mother cell.
Daughter cells formed by meiotic division lead to
the formation of male of female gametes. Each gamete has half the number of
chrosomes of mother cell. During fertilization, the gametes fuse to form
zygote.
In zygote has two sets of chromosomes – one from the male parent
(sperm) and other from female parent
(ovum). Zygote develops into an organism by repeated mitotic divisions.
A CELL with only one set of chromosomes is called a
haploid cell. As the number of chromosomes in the daughter cell are reduced by
half, meiosis is also called reduction dividsion. In general, the male and
female gametes are haploid cells.
In majority of organisms, each cell has two sets of
chromosomes are passed in to the two daughter cells. However, in meisosis only
one of the two sets of chromosomes is passed on to each of the daughter.
During meiosis nucleus divides twice- these division
are called meiosis-I and meiosis-II. In meiosis-I the daughter cells receive
only one set of chromosomes that is reduction in the number of chromosomes
occurs in meiosis-I.
MEIOSIS-II is a simple mitotic division which occurs
immediately after meiosis-I. daughter cells of meiosis-I divide into a second
generation of daughter cells- there are total four daughter cells each of with
only one set chromosomes of four hploid cells are formed at the end of meiosis.
Meiosis –I This occurs in 5 stages .1. Prophase 2. Metaphase 3. Anaphase-I 4. Telophase-I and cytokinesis-I.
1. Prophase -
number of changes occur in the cell during prophase-I. to und prophase-I is
divided into five sub-stages. They are leptotene, zygotene, pacheytene,
diplotene,and diakinesis. Chromatin in the nucleus of the mother cell condenses
and forms chromosomes.
Following this, chromosomes start pairing. Each pair has
two identical chromosomes. One chromosome of the pair is derived from the
father and the ofther from the mother. In this stage, appear like letter’X’.
this is called crossing over the chromosomes move towards the centre of the
cell. Centrioles also move to the opposite ends over to the cell and spindle fibre formation begins. Nucler
envelope and nuleous disappear.
Chromosomeal movement is completed. Chromosomes lie
in the centre of the cell in the form pf plate- called quatorial plate. Some of
the spindle fibres are attached to the centromere of the chromosome and rest of
the spindle fibres attach to the centrosome of the opposite end of the cell.
Length of spindle fibres is reduced. As a result
chromosome are pulled apart. Each chromosomes splits into two sister chromosomes. Each sister chromosomes has a
segment of chromatid derived from mother cell and the father cell. Chromosome
move towards opposite end of the cell.
Chromosomal movement towards opposite poles of the
cells completed. Spindle fibres disappear.
Nuclear envelope reappears around chromosomes and the nucleus is also
formed again. With these meiosis-I is completed and the diploid parental cells
has given rise to daughters cells with haploid
numbers of chromosomes.
This is the second division nuceus in meiosis.
Haploid daughter cells formed in meiosis-I participate in this division and as
parental cells. They divide to produce two haploid daughter cells each. Before
dividing, chromosomal number of the haploid cell doubles. As the end of
meiosis-II four haploid daughter cells are formed. meiosis-II also proceeds in
stages – prophase-II 2.
Metaphas--II 3.
Anaphase-II 4. Telophase-II and cytokinesis-II .
This division
is similar to mitotic division.. you may refer the chapter on mitosis for the
change in the cell that occur in this division and for the process of cell
division.
Points to
remember-
During meiosis, only one set of chromosomes are
passed on to the daughter cells. Hence daughter cells have hald the number of
the chromosomes of the mother cell.
In meiosis , karyokinesi and cytokinesis occur two
times.
Chromosomes number is not doubled during meiosis-I .
during this division, the chromosomes number is reduced by half. The diploid
mother cell gives to two haploid daughter cells.
Prophase-I of meiosis is divided into five
sub-stages.
Before meiosis-II, chromosomes number is doubled and
the haploid mother cell gives rise to two haploid daughter cells.
The events in meiosis-II are similar to mitotic
division.
Crossing over of chromosomes occur during meiosis.
THANKYOU,
 Nanditha completed her Masters in Zoology, English, and Education. She is multifaceted and has an abiding interest in children and education. She is a vibrant and enthusiastic teacher and has a unique ability to draw the attention of children to the subject at hand. Her primary goal is to carry out deep studies on the effect of a child centric and holistic education on students. Herself a skilled teacher in multiple subjects she wants her researches to sensitize the world to the infinite powers inherent in the child. She has done a marvelous work in ICT education. Received “International Academic and Research Excellence Award (IARE 2019) by GISR, ‘Research in Education Award’ by EIA-2019, ‘National Education Leadership Award’- 2019, ‘Best Young Researcher Award’ GERA 2019 and ‘South Indian women’s Achiever Award’.
www.sonuacademy.in
www.nrkacademy.com
www.thehindiacademy.com
www.ibcurriculum.in
Nanditha completed her Masters in Zoology, English, and Education. She is multifaceted and has an abiding interest in children and education. She is a vibrant and enthusiastic teacher and has a unique ability to draw the attention of children to the subject at hand. Her primary goal is to carry out deep studies on the effect of a child centric and holistic education on students. Herself a skilled teacher in multiple subjects she wants her researches to sensitize the world to the infinite powers inherent in the child. She has done a marvelous work in ICT education. Received “International Academic and Research Excellence Award (IARE 2019) by GISR, ‘Research in Education Award’ by EIA-2019, ‘National Education Leadership Award’- 2019, ‘Best Young Researcher Award’ GERA 2019 and ‘South Indian women’s Achiever Award’.
www.sonuacademy.in
www.nrkacademy.com
www.thehindiacademy.com
www.ibcurriculum.in
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)