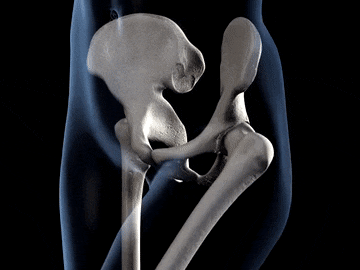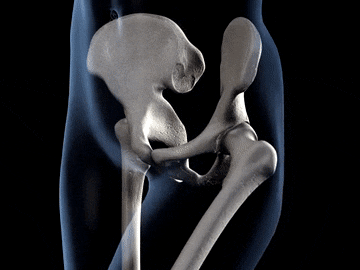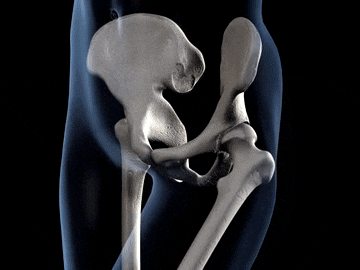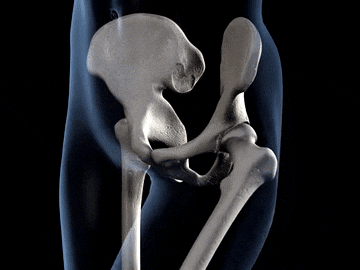
You often feel something hard when you touch your arm your legs and even your Head do you know what the hard substance present insede our body is?? This are the substance called bones. A human body is made up of a number of bones together and this bones form a frame work that gives shape to our body.
The body without skeletal will appear like a jelly that has no shape of its own. Not only does the skeleton gives shape and support it also helps in the movement of various in the body.
In this session you are going to learn about:
· Human Skeletal system
· Movement
· Locomotion
· Bones
· Cartilage
· Types of bones
· Parts of skeletal system
· Joints
· Types of Joints
· Cartilage
· Muscles
HUMAN SKELETON: The framework of bones and cartilage which gives shape and support to the body an animal is called skeleton. Skeletal structure is composed of hard material which is made up of calcium called bones. The human skeleton is made up of 206 bones. In human beings, the skeleton is present in side the body, so it is called endoskeleton.
Movements: A change in the position of any object is called movement. Many movements take place in our body and also in other organisms’ body.
Locomotion: When movement results in change of position of the whole organism, it is called locomotion.
Bones: A baby's body has about 300 bones at birth. These eventually fuse (grow together) to form the 206 bones that adults have. There are 206 bones in the body which form more than 200 joints with each other. While the bones are hard. Bone cells are embedded in a hard matrix composed of calcium and phosphorus compounds
Cartilage is a soft elastic tissue that covers the bones at the region of the joints. It offers support to the structure. It connects the bones together. Cartilage has widely spaced cells suspended in a matrix of proteins and sugars. It is found in the nose, ears, and the rings of the trachea to give flexibility.
Types of bones: Bones can be classified into four types based on their shape:
Long Bones -They are long and slender bones found generally in the limbs. ex. humerus, femur.
Short Bones: They are short bones which are smaller in size and are found in the carpals and tarsals.
Flat Bones: they are thin and flat in nature and not all of them are completely flat. They provide surface area for muscle attachment. Ex: scapula, sternum
Irregular Bones: These bones do not have specific shapes and therefore cannot be put into any other group. Ex: vertebrae
Parts of skeleton
Human skeleton is of two parts, axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton. Axial skeleton includes the skull, vertebral column and the rib cage.
Appendicular skeleton includes shoulder bone, pelvic bone, arm bone, and the leg bone.
Skull: Bony part of our head is called skull. The skull is made up of 22 bony plates joined together. The skull is at the top of the vertebral column. It is composed of two main parts. 1. Cranium 2. Facial bones.
Cranium: The cranium gives protection to the brain. The bones of the cranium are flat and are held firmly in a Zipper- like manner. The joints of the cranial bones are fused joints.
Facial bones: These bones make the front and the lower part of the skull. The lower jaw bone or mandible is
Backbone or Vertebral Column: The back bone is a long hollow, rod like structure running from the base of the skull to the hip, inside our body. The scientific name of back bone is Vertebral Column. It consists of 33 small rings; called vertebrae. Between various vertebrae of back bone are present with the disc like structure called cartilage i.e made up of soft bones. Our backbone supports the head its top. The shoulder bones, rib bones and hip bones are all joined to the black bone.
Each vertebra has a hole in it. Due to this, there is hollow centre inside the backbone. Thus back bone encloses and protects the spinal cord from the damage.
Chest bone or Rib Cage: Sternum or chest bone, is a flat bone at the center of the chest. The ribs and sternum make up what is called the ‘ribcage’. Rib cage occupies the chest region. It is cone-shaped structure made up of 12 pairs of ribs. Ribs are attached to vertebrae at the back which curve around to form a cage. 10 pairs of ribs are attached to the breast bone at the front.
Floating ribs are ribs that are not attached to the sternum (the breast bone) or to other ribs. 2 pairs of lower ribs are free at front. These are called as free-floating ribs. Rib cage is set up in such a way that it can contract and expand during the process of breathing. Rib cage protects the underlying lungs, heart and some part of liver etc.
Shoulder bone or Pectoral Girdle: The shoulder bone is formed by the collar bone and the shoulder blade. It is attached to the upper part of the rib-cage and to the upper arm bone. The shoulder blade is attached to backbone by muscles to allow the free movement of the shoulder.
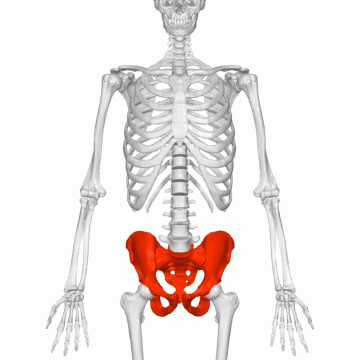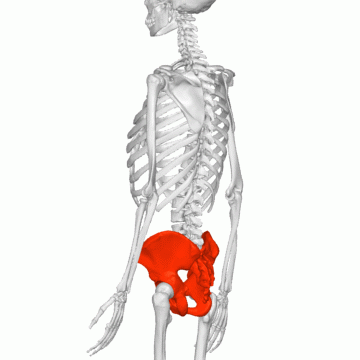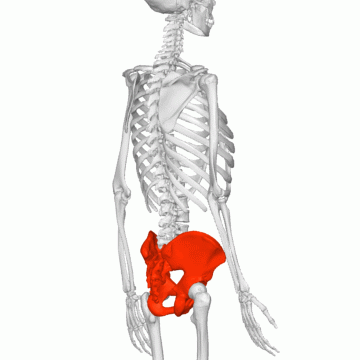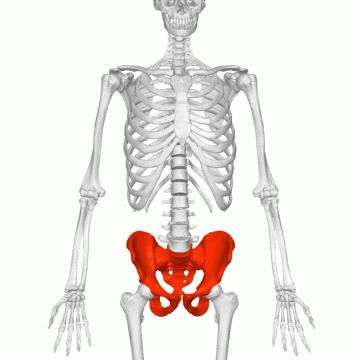
Hip Bone or Pelvic Girdle:The hip bone forms a large, basin shape framework at the lower end of the back bone, to which the legs are attached. The hip bone is also known as pelvic bone. It is made of number of bones fused together by fixed joints. The thigh bones of our legs are joined to the hip bone by ball and socket joints.
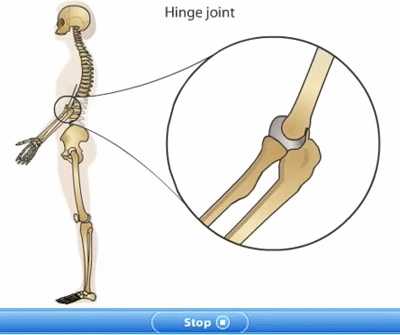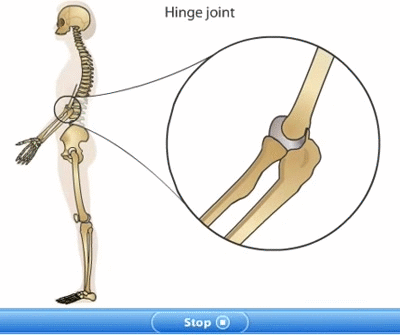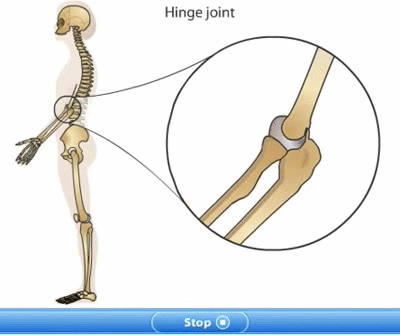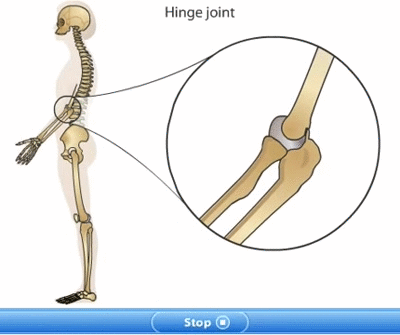
Bones of hands and legs: The upper limb of human body from the shoulder to the hand is called an arm. There are two arms in skeleton. The two arms are attached to the shoulder blades of the skeleton by ball and socket joints. Each arm consists of three parts. The upper arm, lower arm and hand. The upper is from shoulder to elbow. The upper arm consists of single bone called Humerus. The lower arm is from elbow to wrist. The lower arm is made up of two bones: radius and ulna. The upper arm bones connect to lower arm bones by hinge joint at the elbow. The hand consists of various small bones which form wrist, palm and fingers.
The lower limbs of the body on which person walks on stands are called legs. There are two legs in the human body. The two legs are attached to hip bone of skeleton by ball and socket joints. Each leg consists of three parts: upper leg, lower leg and foot. The upper leg is from hip to knee. The upper leg consists of single bone called femur or thigh bone. Wrist is made up of carpals. Palm is made up of metacarpals. Fingers are made up of phalanges.
The lower leg is from knee to ankle. The lower leg consists of two bones: tibia and fibula. The upper leg bone connects to lower leg bones with hinge join. There is also a knee cap called patella. The foot consists of various small bones which form ankle, middle part of foot and toes. Ankle is made up of tarsals. Foot is made up of metatarsals. Toes are made up of phalanges.
Joints: The location where two or more bones meet is called a joint. Ligaments bind a bone to another bone. Tendons bind a bone to a muscle.
Types of Joints
Fixed joints: The joints where no movement of bones is possible are called fixed joint. The joints in the skull bone (cranium) are examples of fixed or immovable joints.
Moveable joint: Movement is possible in these joints. Freely movable joints and partially movable joints. There are four types of movable joints in the body; which are as follows:
Ball and socket joint: In this joint the rounded end of one bone fits into the cavity (hollow space) of another bone. It permits movement in all directions. The joints between shoulder and the upper arm is an example of ball and socket joint. Similarly, the joint between thigh and hip is an example of ball and socket joint.
Pivot Joint: Pivotal joints allow for rotation, twisting, extension, and flexibility. This is the joint where our neck joints head and allow the movement of forward, backward, left and right direction. It is moreover like a cylindrical bone moving in a ring. Ex:Head & Arms.
Hinge joint: Hinge joints are found between the two or more than two bones where we need back and forth movement. This joint is similar to the hinges in a door. This joint allows movement only in one plane and only up to 1800. The knee joint and elbow joint are examples of hinge joint. E.g. Elbows and Knees.. For example: knees, elbow, ankle joints.
Muscles: Muscles are attached to the bones and is responsible for the movement of human body. There is change in the length of muscle due to contraction and relaxation. If you move your arm touching your shoulder you will observe the bulging part on your arm, this is muscle due to contraction and it come back to its normal position if you stretch your arm and muscle come to relax.
THANK YOU